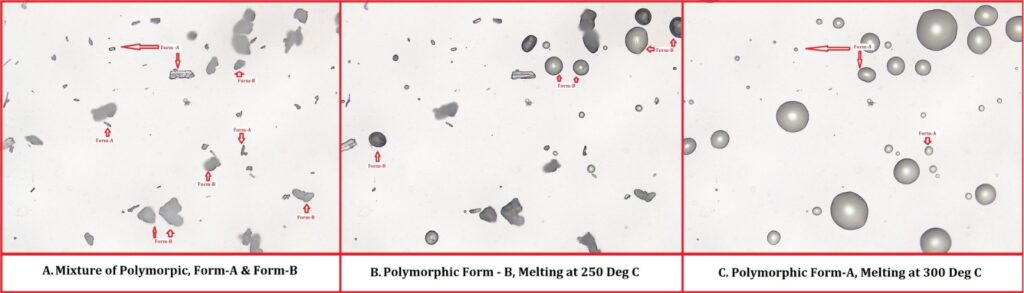
Polymorphism is the ability of a single chemical substance to exist in multiple crystal structures, each with its own unique physical and chemical properties. Polymorphism is a critical aspect of pharmaceutical development as it will significantly impact the physical and chemical properties of a drug substance. Understanding and controlling polymorphism is therefore essential for ensuring the quality and stability of the final product.
Hot stage microscopy (HSM) allows for the real-time observation of thermal transitions of a material, providing valuable information about the thermal behaviour of the material. The ability to control the temperature of the sample during the analysis makes HSM an ideal tool for the study of polymorphism. In this article, I will discuss the application of HSM in the characterization of polymorphic forms.
In addition to their impact on the physical and chemical properties of a drug substance, polymorphs can also present challenges during the manufacturing process. For example, the formation of a less stable polymorph can lead to the degradation of the API, reducing its quality and stability. Understanding the different polymorphic forms and their behaviour under various conditions is therefore essential for ensuring the quality of pharmaceutical products.
Advantages of Hot Stage Microscopy
Hot-stage microscopy (HSM) is a valuable tool for the characterization of materials in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly for the study of polymorphism. The key advantage of HSM is its ability to observe thermal transitions in real time, providing valuable information about the thermal behaviour and stability of the material. HSM also allows for the precise control of temperature during the analysis, making it an ideal tool for the study of polymorphism.
Some of the key benefits of using HSM in polymorphic studies include:
- Real-time observation of thermal transitions: HSM allows for the real-time observation of thermal transitions of a material, providing valuable information about the thermal behaviour and stability of the material.
- Precise temperature control: The ability to control the temperature of the sample during the analysis is critical for the study of polymorphism. HSM allows for the precise control of temperature, making it an ideal tool for the study of polymorphism.
- Ease of use: HSM is a relatively simple technique to use and does not require specialized training or equipment. This makes it accessible to many pharmaceutical researchers and practitioners.
- Versatility: HSM can be used for a wide range of materials, including solid, liquid and semi-solid samples, making it a versatile tool for polymorphic studies.
- Reliable results: The ability to observe thermal transitions in real-time and control temperature during the analysis makes HSM a reliable tool for the study of polymorphism. The results obtained from HSM are highly reproducible and can be used to make informed decisions about product development.
Steps of Polymorphic Characterization using HSM
The following are the steps involved in polymorphic characterization using hot-stage microscopy (HSM):
- Sample preparation: The first step in HSM is to prepare the sample for analysis. This typically involves taking a few trials of wet and dry sampling. Few samples are better observed in the wet method (Glycerol is used) and few are in the dry method. The selection of the method should be done based on the optical properties of the sample and the physicochemical properties of the sample. In the dry method, powdered samples are directly sprinkled on a slide and observed under HSM. Whereas, in the wet method glycerol is added to the sample sprinkled powder and a coverslip is placed on top and observed under HSM.
- Temperature ramping: The temperature of the sample is then slowly increased. Temperature ramping is critical for polymorphic characterization studies as at high ramping the thermal events are overlapped or some of them are missed. It is always preferable to select the slow ramp possible. The temperature ramping rate is carefully controlled to ensure that the sample undergoes thermal transitions in a controlled manner.
- Observing thermal transitions: As the temperature of the sample is increased, thermal transitions can be observed in real-time using the microscope. The appearance of the sample changes as it undergoes these transitions, allowing for the identification of different polymorphic forms.
- Characterization of polymorphic forms: The different polymorphic forms can be characterized based on the appearance of the sample (Crystal structure) during the thermal transitions. This includes the identification of the crystal structure, the melting point, and the thermal stability of the different polymorphic forms.
- Analysis of data: The data obtained from the HSM analysis is then analysed to determine the different polymorphic forms present in the sample and their thermal behaviour. This data can be used to make informed decisions about product development.
- Validation: The results obtained from the HSM analysis are then validated using additional techniques, such as X-ray crystallography (XRD) or differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Raman microscope. These techniques can provide additional information about the crystal structure and thermal behaviour of the different polymorphic forms.
Applications of HSM in Polymorphic Studies
Hot-stage microscopy (HSM) is an innovative tool for the characterization of APIs in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly for the study of polymorphism. Polymorphism can have a significant impact on the physical properties, stability and bioavailability of an API, making it important to understand and control.
Some of the key applications of HSM in polymorphic studies include:
- Identification of polymorphic forms: HSM allows the real-time observation of thermal events of a sample, making it possible to identify the different polymorphic forms present in a sample.
- Analysis of thermal behaviour: The ability to control the temperature of the sample during the analysis makes HSM an ideal tool for the study of the thermal behaviour of polymorphic forms.
- Assessment of stability: The thermal behaviour of polymorphic forms can provide valuable information about the stability of the different forms. HSM allows for precise control over temperature during the analysis, making it possible to determine the stability of the different forms at different temperatures and over time.
- Quality control: HSM can be used as a quality control tool to ensure that the different polymorphic forms are consistent and stable in a sample.
- Process optimization: HSM can also be used in the optimization of processes for the manufacture of APIs.

0 Comments